Libris Location Services
Distributor/Dealer Overview
What are location services?
Libris is equipped with a GPS (Global Positioning System), WiFi SSID Mapping and Location Based Services (LBS) technologies that approximate user location, allowing emergency services to find the Libris user if they are not able to provide their location to the call center.
When does Libris determine location?
There are two instances when Libris approximates a user’s location, also known as a fix.
- Interval Fix is when Libris establishes location at a default interval every ten minutes (interval period can be customized by the call center). The resulting information is stored on the device and is not viewable until Libris is docked in the charger or a call is made.
- Active Call Fix is when Libris establishes user location during an active call. An active call can be initiated in three ways: the user presses the call button, the call center initiates a call from the device, or a fall automatically triggers a call. Libris attempts to acquire a GPS satellite fix every five seconds during an active call.
How do the three location technologies work?
Satellite
This is the most accurate means of approximating user location. There are 2 ways that Libris obtains GPS information. The first method is called Autonomous GPS. For Autonomous GPS, the GPS antenna inside Libris scans the sky to receive signals from GPS satellites rotating around the Earth, which can take up to three minutes. The second method is called Assisted GPS. For Assisted GPS, Libris receives necessary satellite information from the network so it knows what specific satellites to look for instead of having to scan the sky.
If the location interval has been set to a frequent period, such as 10 minutes, the GPS module can keep track of satellites it has previously located and take less time to obtain a fix. When Libris becomes unable to communicate with a satellite since satellites are always in movement, Libris either needs to rescan the sky or re-receive satellite information from the network.
WiFi
WiFi SSID mapping use multiple WiFi access points to determine a user’s location during an active call. The SSIDs of these access points, along with the signal strength are sent to Google’s access points database via an API. Google returns corresponding location coordinates that display on the map.
LBS or Network
Libris uses a back-end service from the network operator (such as AT&T) to help determine a user’s location during an active call and when satellite and WiFi fixes are not available. LBS (Location Based Services, also referred to as network fix, cellular identification (CID), enhanced cellular identification (eCID), or triangulation) works by using the cell phone number associated with Libris to approximate location relative to nearby cell towers.
What are the steps involved in determining location?
For an Interval Fix
Libris attempts to scan the sky to locate satellite signals in order to calculate a location. It waits up to 3 minutes to locate the satellite signals. There are 2 possible outcomes:
- A satellite fix – Libris is able to locate satellite signals and generate a location fix event.
- No satellite fix – Libris is not able to obtain the satellite signals necessary to calculate a fix, and nothing will be reported or uploaded related to location.
For an Active Call Fix
- During an active call, the last known location of the user will populate the mapping screen only if the location was a satellite fix established less than 15 minutes before the start of the call. Up to 5 of the last known satellite locations over the previous 24 hours before the call are also displayed on the map.
- If a recent satellite fix is not available, Libris will seek out access points and attempt to get a WiFi fix.
- If nether GPS nor WiFi are available, Libris will prompt the network operator’s LBS service to receive a network location approximation based on the device’s proximity to known cell phone towers. If a network location is obtained, it will be displayed on the map with a 500-meter radius red circle.
- During the entire length of the call, the Libris device will repeat the above steps to obtain the best location information.
- In optimal conditions, the active call screen is updated every 5 seconds with a new satellite location fix. If no new location fix of any type is acquired during the active call, then the last known location of the user remains displayed, if available. Otherwise, a message that says, “Acquiring GPS location” will be displayed. Libris will attempt to find a GPS location throughout the entire length of the call.
Summary of location fix technologies in use on Libris
Technology |
Accuracy |
Method |
Libris Use Case |
Limitations |
Satellite |
Highest |
GPS antenna receiving signals from GPS satellites |
Prioritized during both interval fixes and active fall |
Inside buildings, dense urban areas, cloudy weather, terrain, electronic interference |
WiFi SID Mapping |
Moderate |
Uses SSID access points |
Next priority if GPS is not available |
Device can pick up multiple access points |
Location Based Services (network) |
Lowest |
Network operator tower location from back-end service |
Unable to establish satellite fix or WiFi during an active call |
LBS providers’ accuracy of cell network tower locations |
How accurate are the location services?
A satellite fix usually approximates a location to within 50m or less of the device’s actual location, and is denoted on our Libris dashboard map by a blue pin. Clicking on this pin will reveal Libris’ approximate address.
Accuracy increases with the number of GPS satellite signals the Libris GPS antenna receives. Libris constantly searches for and prioritizes location fixes determined by satellite. The optimal conditions in which to establish a satellite fix are outside in an open area with a clear sky. Conditions that reduce satellite fix accuracy include structural obstruction (being inside a commercial building or, to a lesser extent, a home), urban density and cloudy weather.
 Satellite fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call Page map
Satellite fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call Page map
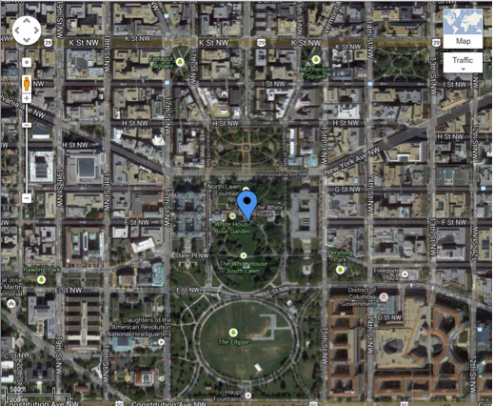
A WiFi fix approximates to within 150 to 300 feet of the device. It is denoted on our Libris Active Call page map by a magenta pin and circle. Clicking on this pin will reveal Libris’ approximate location. The device can pick up multiple WiFi access points and will display the location based on the access point with the best signal strength. The circle represents the approximate area within which the device may be located.
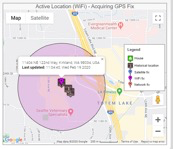 WiFi fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call Page map
WiFi fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call Page map
An LBS or network fix usually approximates to within 1000m of the device’s actual location. This location fix type is estimated due to the inherent difficulties related to cellular strength. A network fix is denoted on our Libris Active Call page map by a red pin surrounded by a red circle. This red circle identifies the approximate area in which Libris in located; the size of the circle will not adjust with increased accuracy, and the center point of this circle does not necessarily indicate Libris’ location. Clicking on this pin will not provide an exact address, but it will provide the name of the neighborhood.
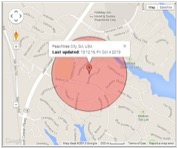 Network fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call page map
Network fix, as seen on the Libris Active Call page map
NOTE:
Location fixes (acquired by either GPS satellite, WiFi or network) are a tool to help determine physical user location. Ultimately, it is a human decision to decide how much to trust a particular type of fix over another. It is always recommended that user location be verbally verified before sending emergency help or ending an emergency call.